Automotive glass
Types, manufacturing, benefits and innovations

The glass in your vehicle’s windshield and windows can do more than just protect you from the elements. Automotive glass has a range of properties and features that help improve visibility and keep you and your passengers safe and comfortable.
Manufacturing auto glass involves complex technical processes. Creating windshields, back glass, side windows, or sunroofs that can withstand driving conditions and meet safety standards requires close collaboration between vehicle glass suppliers and automotive glass manufacturers.
Modern automotive glass is an advanced product with a fascinating history. We explain what automotive glass is made of, how it is manufactured, and explore the different types of automotive glass.
- What is the difference between normal glass and automotive glass?
- A quick guide to the history of automotive glass
- What are the raw materials of automotive glass?
- How do automotive glass processors shape glass?
- What are the properties of automotive glass?
- What are the different types of automotive glass?
- Safety standards in auto glass manufacturing

What is the difference between normal glass and automotive glass?
The term "standard glass" usually refers to annealed float glass, the foundational glass produced from the float process. It provides good optical clarity and serves as the base for high value-added glass products. From this starting point, the glass can be further processed, for example through heat treatment (tempering), lamination, or the addition of coatings, to deliver enhanced properties such as safety, strength, or energy performance.
The main difference between standard architectural glass and automotive glass lies in thickness. Standard glass, such as that often used for home windows, is typically 4 mm float glass or more. Automotive glass is produced in thinner sheets, usually 2.1 mm and 3.2 mm, to meet vehicle design and weight requirements.
At this stage, the glass is a simple float glass, most of the time tinted, with no coatings. The glass must undergo further processing, such as shaping, tempering, or laminating, before it is suitable for use in automotive applications.
A quick guide to the history of automotive glass
The very first automotive windshields were introduced in the early 1900s. These products were made of flat, monolithic annealed glass. While they provided basic protection from wind, this type of glass was a safety hazard. When struck by debris, early windshields could easily shatter into large, sharp shards.
To improve safety, manufacturers eventually adopted tempered glass. Tempered glass is stronger than annealed glass, and shatters into many small pieces rather than large shards when broken. However, tempered glass was not a safe option. When broken, the fragments could still cause injuries to the driver or passengers. What’s more, the entire opening was left exposed, making the vehicle difficult to drive.
In the 1980s, laminated glass became mandatory for automotive windshields. The properties of laminated glass mean that even though it may still break, deform, or even be perforated when struck by a projectile, the windshield stays within the frame. An interlayer holds the broken fragments together. The stability of laminated glass reduces the risk of injury due to broken glass and maintains structural integrity.
Today, high-end vehicles might use laminated glass for side windows, for safety reasons, but also to help enhance acoustic comfort by reducing noise. However, regulations and safety considerations require that at least one window remains tempered (non-laminated). In the event of an accident, rescuers can therefore quickly break the glass to extract passengers.
What are the raw materials of automotive glass?
Both standard glass and automotive glass are made from the same basic raw materials and produced through the same float glass process. Glass is made by melting mainly silica sand, soda ash, limestone and dolomite, and floating this molten glass on a tin bath to give it its flat and uniform shape – this is why the process is called the float glass process. Small amounts of metal oxides can be added to the raw materials to tint the glass.
Producing float glass requires expertise and precision to help provide consistent product quality — a requirement that becomes even more critical when the glass is further processed into high-value products such as automotive glass, where surface imperfections or optical distortions could compromise performance and safety. Guardian Glass applies rigorous quality controls throughout the float glass process to deliver the optical clarity and reliability that advanced applications demand.
Automotive glass undergoes additional treatments such as tempering, bending or laminating. Guardian Glass can also add energy efficiency properties by applying a coating on the glass surface, using the sputter magnetron process, similarly to solar control and low-emissivity (low-E) glass used in architectural applications.
Guardian Glass can produce a range of tinted and coated glass, offering a wide range of properties and performances. This flexibility allows our products to be used in a wide variety of applications for architectural projects and the automotive industry.
How do automotive glass processors shape glass?
Glass manufacturers produce float glass that is used by glass processors to produce automotive windshields and windows. The float glass is supplied in flat sheets and must be shaped to fit the specific contours of each vehicle model.
Achieving the perfect fit requires several steps. The glass is initially cut, grinded and 3D bended to fit the needed shape perfectly. Further processes, including painting, tempering and lamination, are applied as needed.
What are the properties of automotive glass?
Automotive glass is a critical part of any vehicle’s design and performance. It goes far beyond basic weather protection — contributing to safety, visibility, comfort, structural integrity, and energy efficiency. Below are the key benefits it provides:
Safety and protection
Safety is a high priority in automotive glass design. Windshields must be laminated to prevent shattering on impact and reduce the risk of injury during accidents. The glass must also have high strength and durability to withstand daily wear and potential impacts from debris. Additionally, automotive glass contributes to the structural integrity of the vehicle.
Clear visibility
Good visibility is essential for safe driving. Automotive glass must offer excellent optical clarity and achieve a minimum of 70% light transmission, as required by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) regulation ECE R43 for windshields and front side windows. Automotive glass is tinted most of the time to help reduce glare. Compared to standard clear glass, tinted glass absorbs more solar energy, helping to reduce the heat transmitted through the glass. With dark tinted glass, it can also offer an added level of privacy for vehicle occupants.
Energy efficiency
Special coatings such as low-emissivity (low-E) coatings can be applied to automotive glass to reduce heat loss through the glass. This is particularly important for electric vehicles, which do not benefit from residual heat produced by a combustion engine and therefore require more energy to heat the interior. By minimizing heat loss through the glass, low-E coatings can help reduce the workload on the heating system, improving cabin comfort and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Acoustic comfort
Some high-end vehicles feature automotive glass with sound-reducing properties to help create a quiet cabin environment. Acoustic interlayers in windshields and side windows reduce the amount of external noise that enters the vehicle. Modern glass is compatible with advanced technologies. Automotive manufacturers now can produce sunroofs with integrated LEDs or electrochromic panels that switch from transparent to opaque.
What are the different types of automotive glass?
While automotive glass is made from the same base materials as standard glass, it is further processed to provide safety, strength, and durability.
There are two main types of glass used in the auto industry: tempered glass and laminated glass.
Tempered glass is strong and shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact. It is primarily used for side and rear windows in vehicles. Laminated glass holds together when broken and is commonly used for windshields and panoramic sunroofs.
Safety standards in auto glass manufacturing
Automotive glass must protect passengers and maintain the vehicle’s structure in an accident. It is subject to strict safety standards.
In the United States, automotive glass must meet ANSI Z26.1, which sets requirements for strength, impact resistance, and light transmission.
In Europe, ECE R43 defines similar rules, including minimum light transmission and shatter behavior.
These standards help ensure that windshields are strong, safe, and provide clear visibility to help reduce injuries in accidents and improve overall driving experience.

Guardian Glass has been connected to the automotive industry since 1932, when we began as a windshield manufacturer. While we no longer produce finished windshields, that experience helped shape our expertise in high-quality automotive glass. Building on that legacy, we’ve continued to innovate and expand our capabilities, delivering advanced glass solutions that can meet the highest standards for safety, performance, and design across a wide range of applications.
-
Guardian® SMG
Guardian® Solar Management Glass (SMG) is an automotive glass that delivers both high light transmission and solar control. This increases visibility and helps reduce the heat inside a vehicle – by absorbing higher levels of solar energy.
See more -
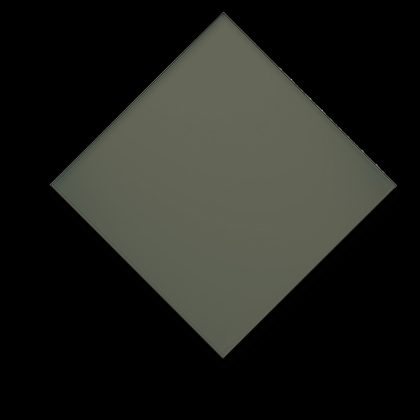

PrivaGuard®
PrivaGuard® is an advanced automotive glass that offers low natural light transmission, reduced solar thermal load and excellent privacy protection. Helping to make a drive more of a pleasure.
See more
